Cryptocurrency meaning
With so many crypto projects and products available, it can be hard to decide which ones are the best fit for your specific needs. Which is why we’ve created an extensive section specifically for reviewing and ranking projects in the market. https://unprintednews.com/the-largest-mosque-in-the-world/ From dApps and staking solutions to Telegram trading bots and exchanges, we provide in-depth reviews and curated top lists to help you confidently choose the right products in the crypto space.
The very first cryptocurrency was Bitcoin. Since it is open source, it is possible for other people to use the majority of the code, make a few changes and then launch their own separate currency. Many people have done exactly this. Some of these coins are very similar to Bitcoin, with just one or two amended features (such as Litecoin), while others are very different, with varying models of security, issuance and governance. However, they all share the same moniker — every coin issued after Bitcoin is considered to be an altcoin.
The investment amount from retail and institutional investors is a huge factor in determining cryptocurrency price. Retail investors can be motivated to buy or sell a particular token because of many things, from technical indicators to rewards of the hype generated by social media.
How does cryptocurrency work
Disclaimer: NerdWallet strives to keep its information accurate and up to date. This information may be different than what you see when you visit a financial institution, service provider or specific product’s site. All financial products, shopping products and services are presented without warranty. When evaluating offers, please review the financial institution’s Terms and Conditions. Pre-qualified offers are not binding. If you find discrepancies with your credit score or information from your credit report, please contact TransUnion® directly.
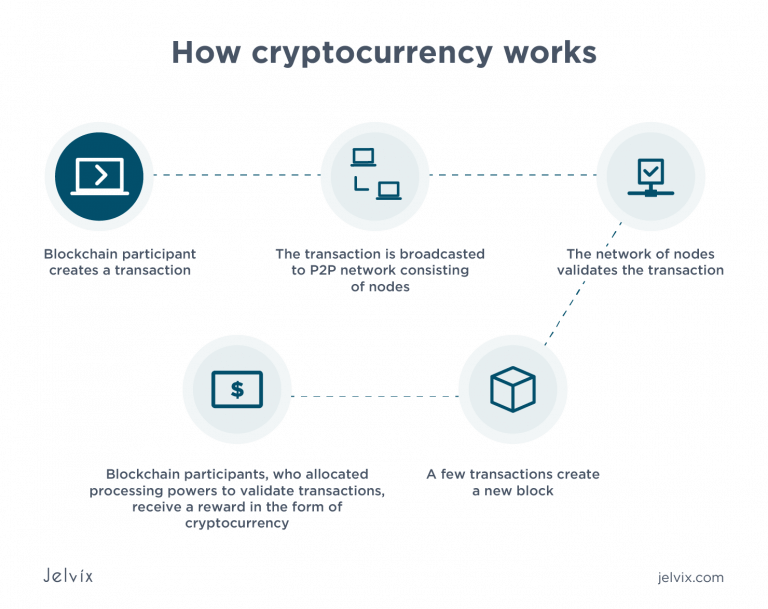
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency secured by cryptography, which makes it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Most cryptocurrencies exist on decentralized networks using blockchain technology—a distributed ledger enforced by a disparate network of computers.
Cryptocurrencies are fungible, meaning the value remains the same when bought, sold, or traded. Cryptocurrency isn’t the same as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) with variable values. For example, one dollar in crypto will always be one dollar, whereas the value of one NFT dollar depends on the digital asset it’s attached to.
Cryptocurrency, or crypto, is a digital payment platform that eliminates the need to carry physical money. It exists only in digital form, and although people mainly use it for online transactions, you can make some physical purchases. Unlike traditional money printed only by the government, several companies sell cryptocurrency.
In contrast, a CBDC could potentially support a number of public policy objectives, including safeguarding public trust in money and promoting efficiency, safety, resilience and innovation in the payment system. The Reserve Bank is continuing to closely examine the case for a CBDC and working with other central banks on this issue. The Reserve Bank is considering the relevant technical issues, as well as the broader policy implications.
Activity in cryptocurrency markets has increased significantly. The fascination with these currencies appears to have been more speculative (buying cryptocurrencies to make a profit) than related to their use as a new and unique system for making payments. Related to this, there has also been a high degree of volatility in the prices of many cryptocurrencies. For example, the price of Bitcoin increased from about US$30,000 in mid 2021 to almost US$70,000 toward the end of 2021 before falling to around US$35,000 in early 2022. Rival cryptocurrencies like Ether have experienced similar volatility. The extraordinary interest in cryptocurrencies has also seen a growing amount of computing power used to solve the complex codes that many of these systems use to help protect them from being corrupted. Despite the increased level of interest in cryptocurrencies, there is scepticism about whether they could ever replace more traditional payment methods or national currencies.
Types of cryptocurrency
In the years since Bitcoin made its debut, thousands of other coins and tokens have been launched. Today’s crypto world encompasses a dazzling array of digital assets with different technical profiles and intended uses.
Proof-of-work cryptocurrencies, such as bitcoin, offer block rewards incentives for miners. There has been an implicit belief that whether miners are paid by block rewards or transaction fees does not affect the security of the blockchain, but a study suggests that this may not be the case under certain circumstances.
That’s not as unrealistic an idea as it sounds. More and more purchases are made electronically, either online or with credit and debit cards. Paper money is rapidly becoming obsolete. Why not use a currency that was designed for online transactions? In fact, several such currencies were created in the 1980s and 1990s. None gathered much of a following until Bitcoin was launched.
The Department of the Treasury, on 20 May 2021, announced that it would require any transfer worth $10,000 or more to be reported to the Internal Revenue Service since cryptocurrency already posed a problem where illegal activity like tax evasion was facilitated broadly. This release from the IRS was a part of efforts to promote better compliance and consider more severe penalties for tax evaders.
The remittance economy is testing one of cryptocurrency’s most prominent use cases. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin serve as intermediate currencies to streamline money transfers across borders. Thus, a fiat currency is converted to Bitcoin (or another cryptocurrency), transferred across borders, and subsequently converted to the destination fiat currency without third-party involvement.
